nostoc-lichen-phylogenomics
Data annotation
Installation of the needed environment in the cluster (Duke University)
I have already installed Conda with the miniconda version inside the cluster in the next directory:
$ /hpc/group/bio1/diego/miniconda3
Then, it is needed to add the channels where most of the biological-usage packages are located. Otherwise, at the moment we try to search for some packages we will obtain that the search got no results:
$ conda config --add channels conda-forge
$ conda config --add channels bioconda
We can procced to install mamba, a tool that will help me to
get compatible dependencies for each of the packages that I am going to install.
$ conda install -c conda-forge mamba
This set up will allow me to make a new environment where I will install Prokka and Antismash, I will call this
environment gmining from genome mining:
$ mamba create -n gmining antismash prokka
after we donwloaded these packages, we need to install some dependencies that Antismash needs, as specified in its page
$ conda activate gmining
$ download-antismash-databases
After this steps we are all set to do the first step of the annotation
Prokka annotation
Prokka is a whole genome annotation tool that has been designed to be used with prokariotyc genomes. This is the first step to manupulate a bin or Metagenome assembled genome (MAG).
Prokka will give us a set of files as the output, in the next image (borrowed from the Prokka page) you can see the information that these files will contain.
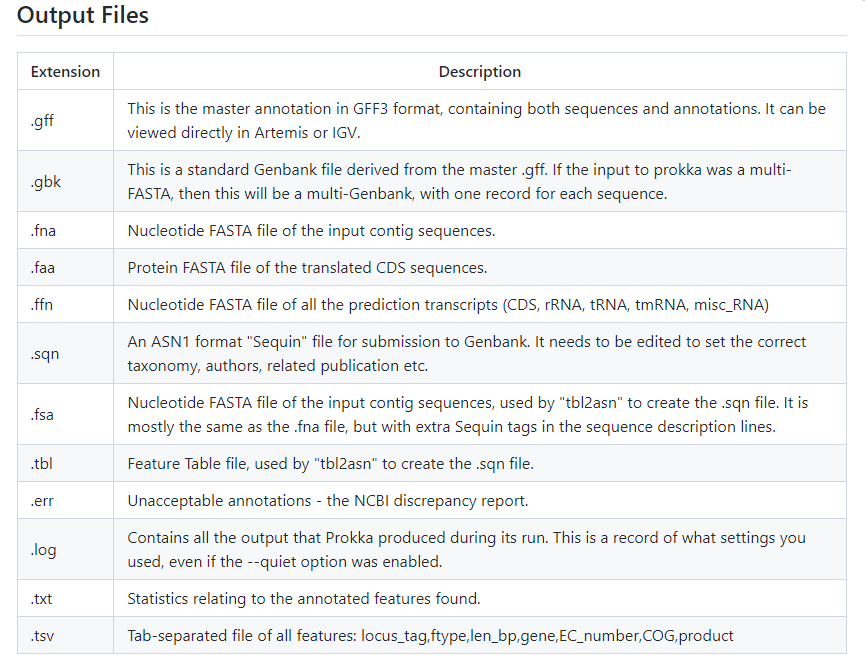
I will be working in the next directory:
- /hpc/group/bio1/diego/cyanos-Carlos
By taking a random bin of the ones that Carlos share with me (P2039_bin.23.fa), I was able to annotate it using Prokka. There was a problem using
the deafult behaviour of this problem. The .gbk file that was generated merged the contig name and the contig lenght. That
generates a error in the parsing process in programs as antismash. I found that you can use the --compliant flag to
make the locus layout comply to the NCBI expected layout. The next line is an example with one of P2039_bin.23.fa bin:
$ prokka --prefix P2039 --outdir P2039 --kingdom Bacteria --genus Nostoc \
--strain P2039 --usegenus --addgenes --metagenome --compliant --cpus 12 carlos-bins/P2039_bin.23.fa
After Prokka completed the run, we will have a new set of files inside the P2039 directory:
P2039.err P2039.ffn P2039.fsa P2039.gff P2039.sqn P2039.tsv
P2039.faa P2039.fna P2039.gbk P2039.log P2039.tbl P2039.txt
All of them are useful for different analyses, but we will be working with the
.gbk files.
Antismash annotation
Having completed a succesful annotation with Prokka, we can now take the next step and use Antismash
to annotate the secondary metabolism of the bins provided.
We will run an example with the already annotated bin P2039:
$ antismash P2039/P2039.gbk --output-dir P2039-antis
The process may take a while depending on the resources that you are using. In the
end we will have a P2039-antis folder with the next set of output-files:
IFKOFEHL_1.region001.gbk IFKOFEHL_16.region001.gbk IFKOFEHL_6.region002.gbk html
IFKOFEHL_1.region002.gbk IFKOFEHL_3.region001.gbk IFKOFEHL_6.region003.gbk images
IFKOFEHL_10.region001.gbk IFKOFEHL_36.region001.gbk P2039.gbk index.html
IFKOFEHL_10.region002.gbk IFKOFEHL_40.region001.gbk P2039.json js
IFKOFEHL_11.region001.gbk IFKOFEHL_48.region001.gbk P2039.zip regions.js
IFKOFEHL_12.region001.gbk IFKOFEHL_6.region001.gbk css svg
To go in detail into all of the contents of this folder, let’s download this folder
to our own computer (assuming that you are doing it in the cluster) and open the
index.html file the internet browse of your election. The page that you will
find will be the next one:
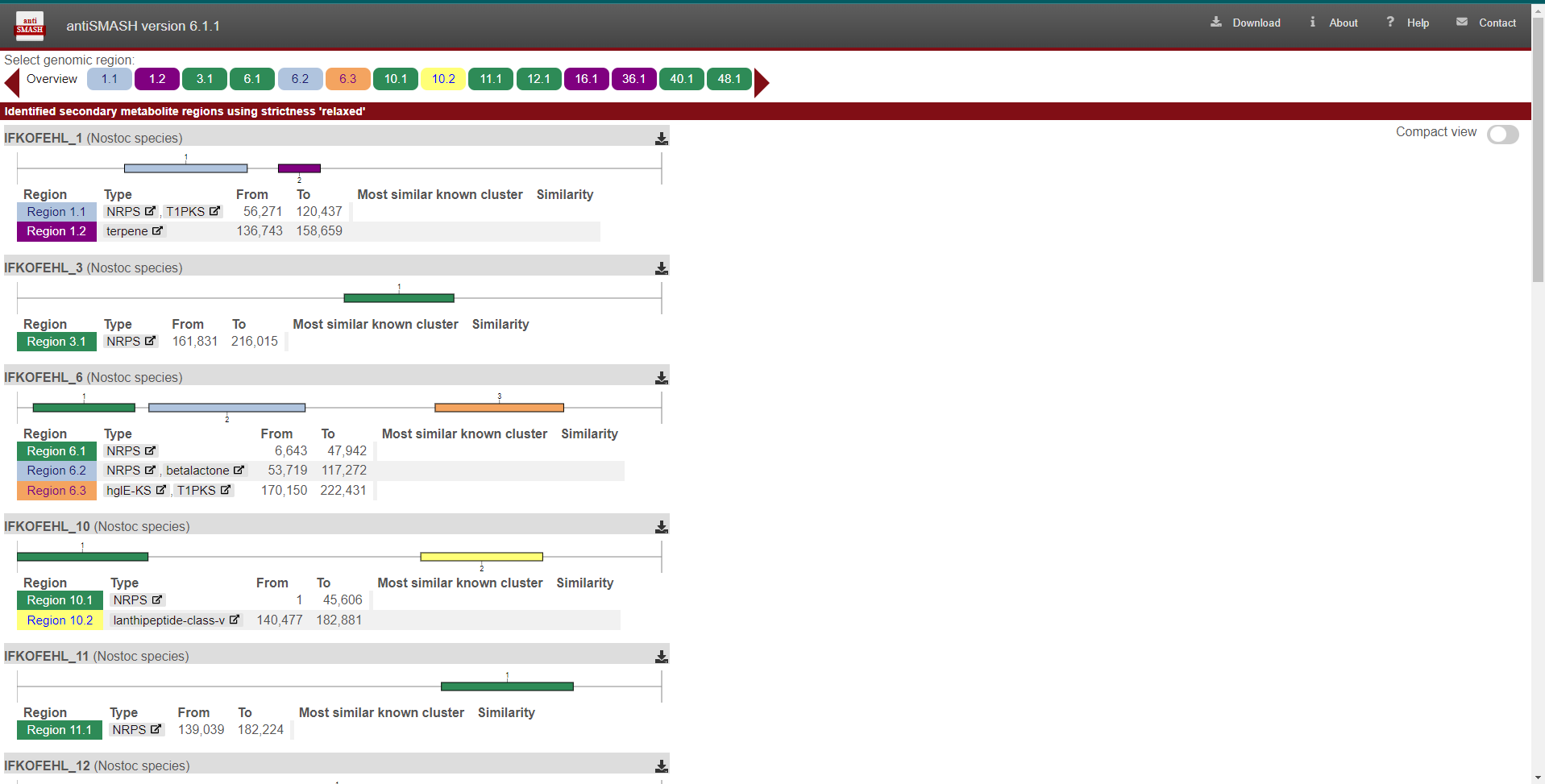
The color rectangles in the upper part symbolize the biosynthetic gene cluster(BGC)
that Antismash found in the P2039 bin. So the first one is named
after the location inside the bin that this BGC was found. So the .gbk file that
will bring the information of this cluster will be IFKOFEHL_1.region001.gbk.
The same applies to the other 14 BGCs. If we click in one of the squares, let’s
say the first one, this page will display a new set of marvels:
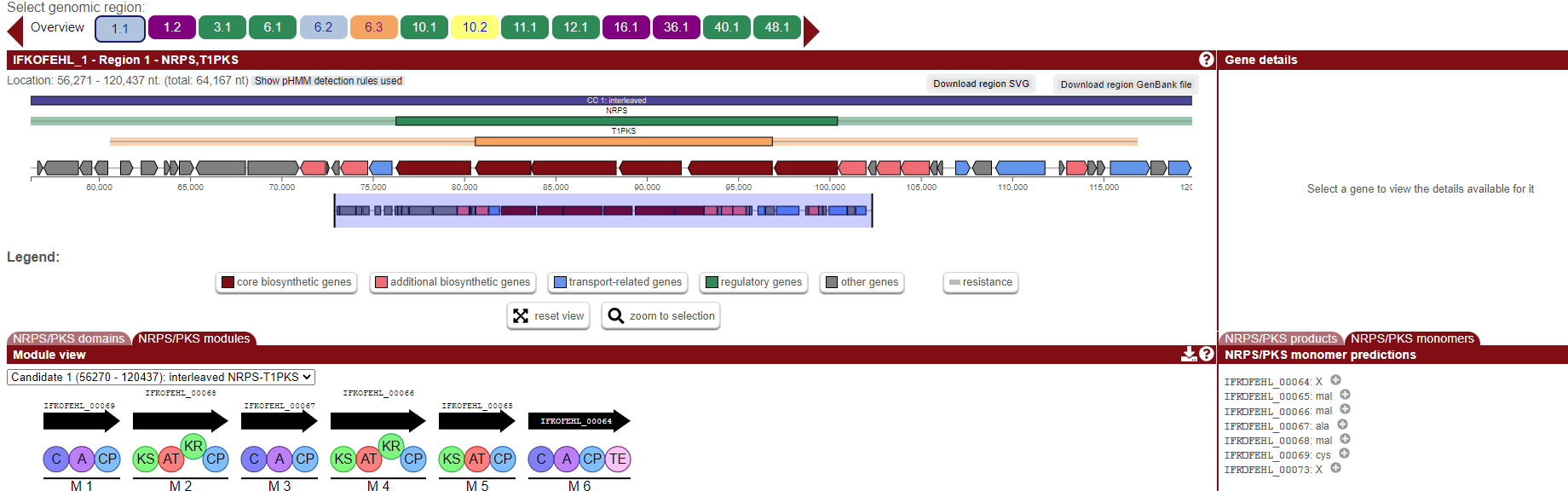
Here we will see the different genes that are part of the BGC represented as arrows. We also can have access to the information of the lenght, sequence and identity of some of these genes.
We have done this for one of the bins, but we would love to automatize this process.
Atomatization of Prokka-Antismash
Now that we have managed to annotate a bin with both Prokka and Antismash, we can
create a script that will submit a job to the cluster (Duke University) and will annotate
all the bins that we want:
#!/bin/bash
#Date of creation: 08/29/2022
#This script will be used to run the annotation of bacterial genomes with Prokka and
#Antismash.
# This little program requires that te user gives the next three parameters:
lgem=$1 #Folder location of the genomes that you want to annotate
pref=$2 #Prefix that you would like for the analysis to have
gus=$3 #If all the genomes that you are going to annotat, are from the same genus put that here
#Here we will declare a variable to hold the actual directory:
root=$(pwd) #Gets the path to the directory of this file, on which the outputs ought to be created
sign='$'
#General directories
mkdir -p $pref-gAnot
mkdir -p $pref-gAnot/logs/script
# Directories for the Prokka analysis
mkdir -p $pref-gAnot/prokka
# Dierectories for the Antismash analysis
mkdir -p $pref-gAnot/antismash
cat <<EOF > runAnnotation.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=16G #The RAM memory that will be asssigned to each threads
#SBATCH -c 16 #The number of threads to be used in this script
#SBATCH --output=$pref-gAnot/logs/$pref-annot.out #A file with the output information will be generated in the location indicated
#SBATCH --error=$pref-gAnot/logs/$pref-annot.err #If a error occurs, a file will be created in the location indicated
#SBATCH --partition=common
source $(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh
conda activate gmining
ls $lgem | while read line; do gen=${sign}(echo ${sign}line | cut -d'_' -f1);
prokka --prefix ${sign}gen --outdir $pref-gAnot/prokka/${sign}gen --kingdom Bacteria --genus $gus \
--strain ${sign}gen --usegenus --addgenes --metagenome --compliant --cpus 16 \
$lgem${sign}gen*;
antismash --asf --pfam2go $pref-gAnot/prokka/${sign}gen/*.gbk -c 16 \
--output-dir $pref-gAnot/antismash/${sign}gen --output-basename ${sign}gen \
--html-title report-${sign}gen --html-start-compact;
done
EOF
sbatch runAnnotation.sh
mv runAnnotation.sh $pref-gAnot/logs/script
The script is asking us to give three different inputs:
- Location of hte folder where the
.fastafiles of the bins are - A prefix of the user choice that will be used to label directories to allocate the outputs
- If all the bins to be annotated are of the same genus (e.g. Nostoc), put it here. Otherwise, leave it blank
I will run the script with the next line of code inside the working directory /hpc/group/bio1/diego/cyanos-Carlos:
$ sh annot.sh carlos-bins/ nostoc Nostoc
At the end of the run (it would take 17 hours more or less), we will have the next set of output folders:
$ ls nostoc-gAnot/antismash/
3 NMS4 P10247 P12502 P12569 P12642 P1574 P2162 P5023 P6636 P8571 P9119 S10 S44 X2
8274 NMS5 P10264 P12521 P12570 P12646 P2037 P2164 P539 P6963 P8575 P9121 S12 S5
8277 NMS7 P1030 P12523 P12573 P12649 P2039 P2170 P607 P6970 P8577 P943 S13 S51
JL23 NMS8 P10324 P12537 P12578 P12650 P2081 P2180 P6447 P8202 P8580 P9639 S24 S52
JL31 NMS9 P10894 P12545 P12584 P14213 P2083 P2213 P6465 P8219 P8690 P9728 S27 S62
JL33 NOS P11060 P12559 P12588 P14264 P2090 P2224 P6524 P8231 P8768 P9820 S31 S66
JL34 P10073 P11388 P12560 P12591 P14269 P2115 P3034 P6600 P8256 P8840 P9822 S32 S67
NMS1 P10160 P11425 P12564 P12639 P14318 P2123 P3068 P6602 P8569 P8857 P9895 S40 S8
NMS2 P10246 P1229 P12567 P12641 P14321 P2152 P330 P6620 P8570 P8926 S1 S43 S9
We have completed the first step wich is annotation.
Results
After inspecting the results from the script submitted to the cluster, I was aware that there are three
bins that do not have an Antismash output:
- NMS5
- P12639
- P6970
I try to re-annotate them using the next little script:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=16G #The RAM memory that will be asssigned to each threads
#SBATCH -c 16 #The number of threads to be used in this script
#SBATCH --output=nostoc-gAnot/logs/some-nostoc.out #A file with the output information will be generated in the location indicated
#SBATCH --error=nostoc-gAnot/logs/some-nostoc.err #If a error occurs, a file will be created in the location indicated
#SBATCH --partition=common
source /hpc/group/bio1/diego/miniconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh
conda activate gmining
for i in NMS5 P12639 P6970;
do antismash --asf --pfam2go nostoc-gAnot/prokka/$i/*.gbk -c 16 --output-dir nostoc-gAnot/antismash/$i --output-basename $i --html-title report-$i --html-start-compact
In the end, I obtained the same result. I figured out that I commited a mistake there are two bins with the name P12639.
Because how I did the script to submit them to the cluster Prokka put only one output in the P12639 folder. Using the
next script I repeated the process for these two bins:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=16G #The RAM memory that will be asssigned to each threads
#SBATCH -c 16 #The number of threads to be used in this script
#SBATCH --output=nostoc-gAnot/logs/some-nostoc.out #A file with the output information will be generated in the location indicated
#SBATCH --error=nostoc-gAnot/logs/some-nostoc.err #If a error occurs, a file will be created in the location indicated
#SBATCH --partition=common
source /hpc/group/bio1/diego/miniconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh
conda activate gmining
ls carlos-bins/P12639* | while read line; do file=$(echo $line | cut -d'/' -f2| cut -d'.' -f1);
prokka --prefix $file --outdir nostoc-gAnot/prokka/$file --kingdom Bacteria --genus Nostoc \
--strain $file --usegenus --addgenes --metagenome --compliant --cpus 16 \
carlos-bins/$file*;
antismash --asf --pfam2go nostoc-gAnot/prokka/$file/*.gbk -c 16 --output-dir nostoc-gAnot/antismash/$file --output-basename $file --html-title report-$file --html-start-compact;
done
This indeed generated two different outputs. Nevertheless, both files do not generated any outputs with Antismash.
I want to see the status of these bins, I used info-pbins.sh little programm to extract some important information of
these bins:
#!/bin/bash
echo -e Bin'\t'Completeness'\t'Contamination'\t'#Bins > problematic-bins.txt
for i in NMS5 P12639_bin.2 P12639_bin.3 P6970;
do comp=$(cat metadata/fullqc_set8.csv | grep $i | cut -d',' -f14);
cont=$(cat metadata/fullqc_set8.csv | grep $i | cut -d',' -f15)
assm=$(cat metadata/fullqc_set8.csv | grep $i | cut -d',' -f19)
echo -e $i'\t'$comp'\t'$cont'\t'$assm >> problematic-bins.txt; done
$ sh info-pbins.sh
$ cat problematic-bins.txt
Bin Completeness Contamination #Bins
NMS5 54.41 1.19 1170
P12639_bin.2 84.48 32.99 2883
P12639_bin.3 30.52 12.93 922
P6970 91.12 0.96 1463
As can be seen in the results, each of these bins have to much contings to be processed by Antismash (> 500). So I will let
them out of the future analyses until we can obtain better assemblies.
